WHO-GMP vs ISO Certification in Pharma – What Is the Difference?
Understanding the Role of Certifications in the Pharma Industry
Certifications play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical industry because medicines directly impact human health and safety. Unlike other manufacturing sectors, pharma companies must follow strict regulatory frameworks to ensure that products are safe, effective, and consistent. WHO-GMP and ISO certifications are two commonly discussed standards, but their purpose, scope, and regulatory value are often misunderstood.
Many pharma businesses assume that ISO certification alone is sufficient to establish quality credibility. However, this misunderstanding can lead to serious compliance gaps, rejected exports, and regulatory penalties. To build a strong foundation, it is essential to clearly understand what WHO-GMP and ISO certifications are designed to achieve and how they differ in real-world pharmaceutical operations.
Key Focus Areas of Pharma Certifications
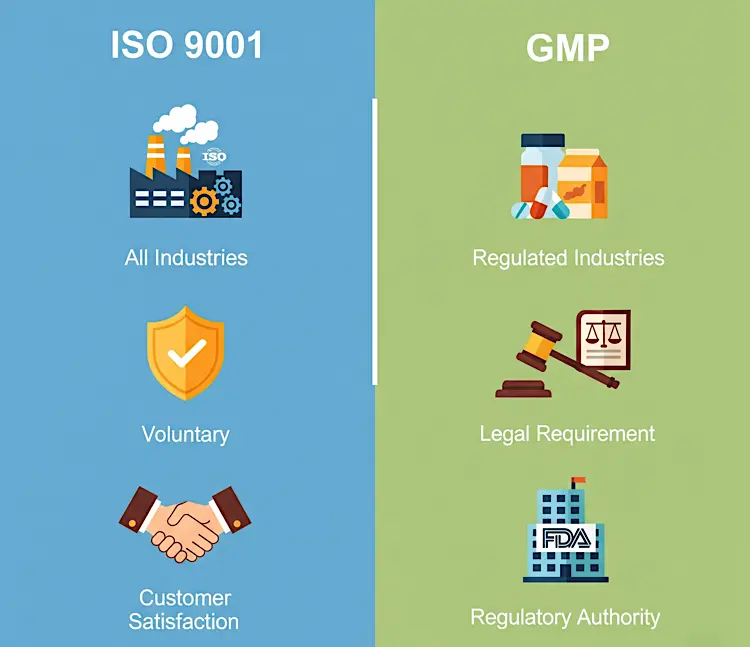
- Patient safety as a priority: Pharma certifications are designed to ensure medicines do not cause harm due to contamination, incorrect dosage, or poor manufacturing practices. WHO-GMP directly addresses these risks, while ISO supports systems that indirectly improve operational consistency.
- Regulatory compliance and legal acceptance: Certifications determine whether a pharmaceutical unit can legally manufacture and supply medicines. WHO-GMP is often a legal requirement, whereas ISO is a voluntary quality management standard.
- Market trust and brand credibility: Certifications build confidence among doctors, distributors, and regulators. WHO-GMP signals regulatory compliance, while ISO reflects management discipline and process stability.
Key Areas Where AI and Automation Impact Pharma Production
Enhancing Efficiency and Reducing Errors
AI and automation streamline operations, reduce human intervention, and minimize errors. From precise formulation measurements to robotic packaging, these technologies ensure consistency and accuracy.
Main Points :
- Automated Formulation Systems : Robots and smart dispensers prepare compounds with precise dosages, eliminating variability.
- Predictive Analytics for Equipment : AI predicts equipment failures and schedules maintenance before downtime occurs.
- Digital Batch Records : Automated recording systems ensure complete traceability and reduce documentation errors.
- Inventory Management : AI-powered tools monitor stock levels, reorder supplies, and prevent shortages.
Additional Points :
- Process Optimization : AI models analyze production data to optimize throughput, reduce waste, and increase yield.
- Energy Efficiency : Automated systems control energy usage in manufacturing plants, reducing operational costs and carbon footprint.
- Faster Production Cycles : Robotics and AI-driven systems accelerate repetitive tasks, speeding up batch production and packaging.
Benefits of AI and Automation in Pharma Production
- Improved Drug Development :
AI algorithms analyze biological and chemical data to identify promising drug candidates, speeding up discovery.
- Enhanced Quality Control :
Automated inspection systems detect deviations and defects in real-time, ensuring compliance with GMP standards.
- Cost Efficiency :
Automation reduces labor-intensive tasks, decreases wastage, and lowers operational costs.
- Regulatory Compliance :
AI tracks regulatory changes, manages documentation, and ensures all processes meet global standards.
- Predictive Maintenance :
Robotic systems equipped with sensors detect potential equipment failures early, reducing downtime and production loss.
- Personalized Medicine :
AI analyzes patient data to support tailored drug formulations, enabling precision therapies.
- Supply Chain Optimization :
Automation streamlines procurement, logistics, and distribution, ensuring timely delivery of medicines.
- Data-Driven Decision Making :
AI provides actionable insights from production data, helping managers make informed operational decisions.
Future of Pharma Production with AI and Automation
Heading: Transforming the Industry for the Next Decade
AI and automation are not just improving current processes—they are shaping the future of pharmaceutical production. Companies like VTV Formulations are investing in AI-powered labs, automated manufacturing units, and intelligent quality control systems to stay ahead in a competitive market.
Key Points :
- Smart Manufacturing Plants : Fully automated plants with AI-driven monitoring systems can operate with minimal human intervention.
- Real-Time Analytics : AI monitors production lines continuously, identifying inefficiencies and suggesting improvements.
- Robotics in Packaging : Automated packaging systems improve speed, reduce contamination risk, and maintain consistent labeling.
- Machine Learning in Forecasting : AI predicts demand fluctuations, helping plan production and inventory more accurately.
- Integration with IoT : Connected devices provide real-time data for better monitoring, maintenance, and quality assurance.
Conclusion
AI and automation are revolutionizing pharmaceutical production, providing benefits such as enhanced efficiency, reduced errors, faster production cycles, and improved compliance. For companies like VTV Formulations, these technologies enable higher-quality products, cost savings, and the ability to meet the ever-growing demand for medicines.
Embracing AI and automation is not merely a technological upgrade—it is a strategic investment for sustainable growth. As the industry continues to evolve, companies that leverage these innovations will be better positioned to deliver safe, effective, and timely medicines while remaining competitive in a dynamic global market.
Explore Related Blogs
Stay informed with our curated selection of similar blogs, offering expert perspectives on pharmaceutical trends, regulatory updates, and product innovations.
These articles are designed to help healthcare professionals, partners, and businesses stay ahead in an ever-evolving industry. Explore more to deepen your knowledge and make informed decisions.